All about crypto mining
Cryptocurrencies traded in public markets suffer from price volatility, so investments require accurate price monitoring. For example, Bitcoin has experienced rapid surges and crashes in its value, climbing to nearly $65,000 in November 2021 before dropping to just over $20,000 a year and a half later https://cherokeeroseenvironmental.com. Bitcoin prices had roared back by mid-2024. As a result of this vast range of volatility, many people consider cryptocurrencies a speculative bubble.
Mining cryptocurrency uses a lot of computer power, so miners are rewarded for the work they do. On the Bitcoin network, miners who confirm new blocks of information are currently rewarded with 6.25 BTC of new Bitcoin. This is why it’s called mining. Instead of mining for gold or coal, crypto miners are digging for new Bitcoin!
In 1983, American cryptographer David Chaum conceived of a type of cryptographic electronic money called ecash. Later, in 1995, he implemented it through Digicash, an early form of cryptographic electronic payments. Digicash required user software in order to withdraw notes from a bank and designate specific encrypted keys before they could be sent to a recipient. This allowed the digital currency to be untraceable by a third party.
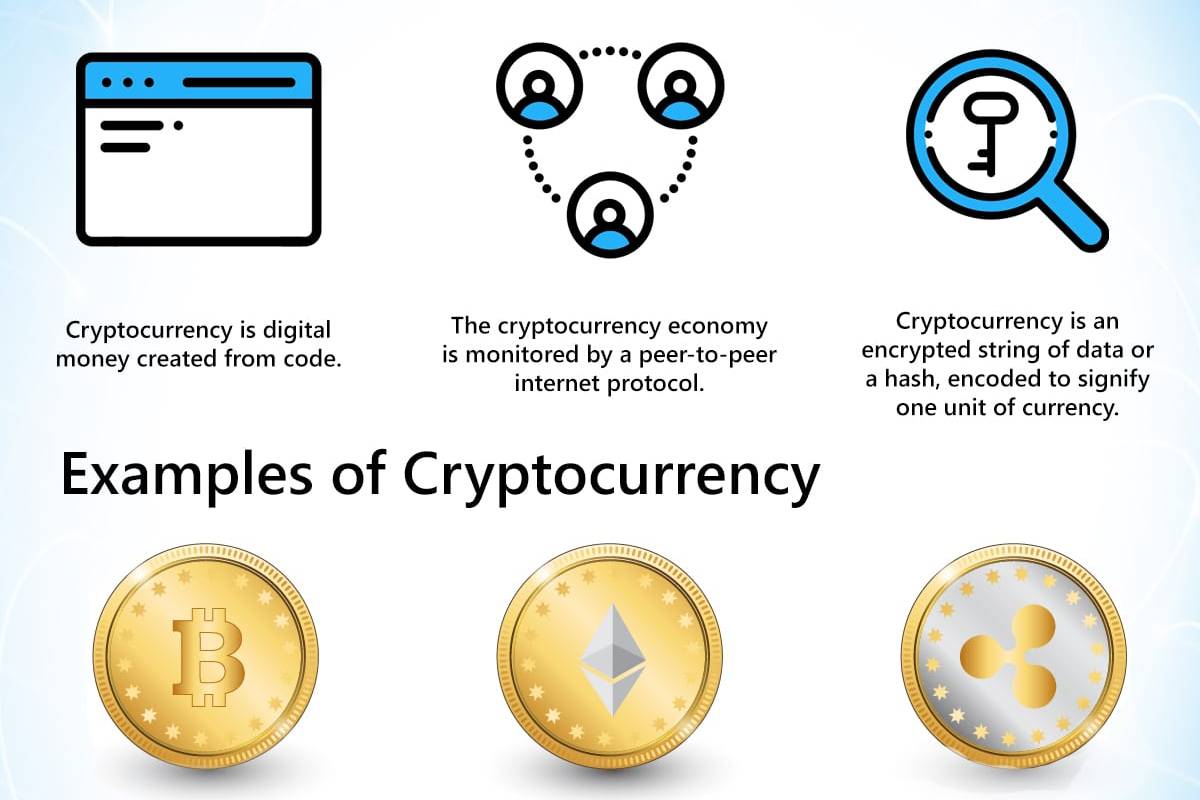
What is crypto currency all about
1. Mining: Cryptocurrencies are generated through a process called Mining. In this process, the miners are required to solve a mathematical puzzle over a specially equipped computer system to be rewarded with bitcoins in exchange.
Crypto purchases with credit cards are considered risky, and some exchanges don’t support them. Some credit card companies don’t allow crypto transactions either. This is because cryptocurrencies are highly volatile, and it is not advisable to risk going into debt — or potentially paying high credit card transaction fees — for certain assets.
Similar criticism was echoed by Auckland University of Technology cryptocurrency specialist and senior lecturer Jeff Nijsse and University of Otago political scientist Professor Robert Patman, who described it as government overreach and described it as inconsistent with international law. Since the Cook Islands is an associated state that is part of the Realm of New Zealand, Patman said that the law would have “implications for New Zealand’s governance arrangements.” A spokesperson for New Zealand Foreign Minister Winston Peters confirmed that New Zealand officials were discussing the legislation with their Cook Islands counterparts. Cook Islands Prime Minister Mark Brown defended the legislation as part of the territory’s fight against international cybercrime.
Individual coin ownership records are stored in a digital ledger or blockchain, which is a computerized database that uses a consensus mechanism to secure transaction records, control the creation of additional coins, and verify the transfer of coin ownership. The two most common consensus mechanisms are proof of work and proof of stake. Despite the name, which has come to describe many of the fungible blockchain tokens that have been created, cryptocurrencies are not considered to be currencies in the traditional sense, and varying legal treatments have been applied to them in various jurisdicitons, including classification as commodities, securities, and currencies. Cryptocurrencies are generally viewed as a distinct asset class in practice.
In September 2021, the government of China, the single largest market for cryptocurrency, declared all cryptocurrency transactions illegal. This completed a crackdown on cryptocurrency that had previously banned the operation of intermediaries and miners within China.
Cryptocurrencies represent a new, decentralized paradigm for money. In this system, centralized intermediaries, such as banks and monetary institutions, are not necessary to enforce trust and police transactions between two parties. Thus, a system with cryptocurrencies eliminates the possibility of a single point of failure—such as a large financial institution setting off a cascade of global crises, such as the one triggered in 2008 by the failure of large investment banks in the U.S.
What is crypto all about
On 18 May 2021, China banned financial institutions and payment companies from being able to provide cryptocurrency transaction related services. This led to a sharp fall in the price of the biggest proof of work cryptocurrencies. For instance, bitcoin fell 31%, Ethereum fell 44%, Binance Coin fell 32% and Dogecoin fell 30%. Proof of work mining was the next focus, with regulators in popular mining regions citing the use of electricity generated from highly polluting sources such as coal to create bitcoin and Ethereum.
Crypto can be a good investment for someone who enjoys speculating and can financially tolerate losing everything invested. However, it is not a wise investment for someone seeking to grow their retirement portfolio or for placing savings into it for growth.
In 1996, the National Security Agency published a paper entitled How to Make a Mint: The Cryptography of Anonymous Electronic Cash, describing a cryptocurrency system. The paper was first published in an MIT mailing list (October 1996) and later (April 1997) in The American Law Review.
According to PricewaterhouseCoopers, four of the 10 biggest proposed initial coin offerings have used Switzerland as a base, where they are frequently registered as non-profit foundations. The Swiss regulatory agency FINMA stated that it would take a “balanced approach” to ICO projects and would allow “legitimate innovators to navigate the regulatory landscape and so launch their projects in a way consistent with national laws protecting investors and the integrity of the financial system.” In response to numerous requests by industry representatives, a legislative ICO working group began to issue legal guidelines in 2018, which are intended to remove uncertainty from cryptocurrency offerings and to establish sustainable business practices.
Otherwise, fraudsters may pose as legitimate virtual currency traders or set up bogus exchanges to trick people into giving them money. Another crypto scam involves fraudulent sales pitches for individual retirement accounts in cryptocurrencies. Then there is straightforward cryptocurrency hacking, where criminals break into the digital wallets where people store their virtual currency to steal it.
